
In simple words, the retained earnings metric reflects the cumulative net income of the company post-adjustments for the distribution of any dividends to shareholders. Retained Earnings on the balance sheet measures the accumulated profits kept by a company to date since inception, rather than issued as dividends. On the balance sheet, retained statement of retained earnings earnings appear in the equity section, separate from share capital. This distinction highlights how much profit has been reinvested versus initially invested by shareholders. The statement of retained earnings provides transparency on how profits are allocated within the business and retained for future growth.
Relation With Income Statement
- This formula considers the beginning retained earnings, net income or profit/loss, and dividends paid.
- Net profit refers to the total revenue generated by a company minus all expenses, taxes, and other costs incurred during a given accounting period.
- For example, outlining the payout ratio and specifying circumstances under which dividends can be reduced can help protect your reinvestment profit.
- In GAAP, the statement of retained earnings can be attached to the income statement, or the balance sheet, or be prepared as a separate financial statement.
- Examples of these items include sales revenue, cost of goods sold, depreciation, and other operating expenses.
Since we have all the balances we need for preparing a statement of changes in equity, it will look like this. Paul’s net income at the end of the year increases the RE account while his dividends decrease the overall the earnings that are kept in the business. Below is a break down of subject weightings in the FMVA® financial analyst program. As you can see there is a heavy focus on financial modeling, finance, Excel, business valuation, budgeting/forecasting, PowerPoint presentations, accounting and business strategy. A company may also use the retained earnings to finance a new product launch to increase the company’s list of product offerings.

How to Calculate Retained Earnings

The last line on the statement sums the total of these adjustments and lists the ending retained earnings balance. The statement of retained earnings is most commonly presented as a separate statement, but can also be appended to the bottom of another financial statement. The retained earnings statement captures changes in retained earnings over a period through a straightforward calculation involving key components. After two years, Company B’s retained earnings are $225,000, all reinvested to fuel its growth without any payouts to shareholders. Calculating retained earnings after a stock dividend involves a few extra steps to figure out the actual amount of dividends you’ll be distributing. Retained earnings are like a running tally of how much profit your company has managed to hold onto since it was founded.

Does retained earnings have a credit balance?
- To actually leverage the power of a statement of retained earnings, you must first know how the formula works.
- The amount of retained earnings that a corporation may pay as cash dividends may be less than total retained earnings for several contractual or voluntary reasons.
- This involves adding the net income or subtracting any net loss reported from the opening balance, followed by deducting dividends.
- The retained earnings are calculated by adding net income to (or subtracting net losses from) the previous term’s retained earnings and then subtracting any net dividend(s) paid to the shareholders.
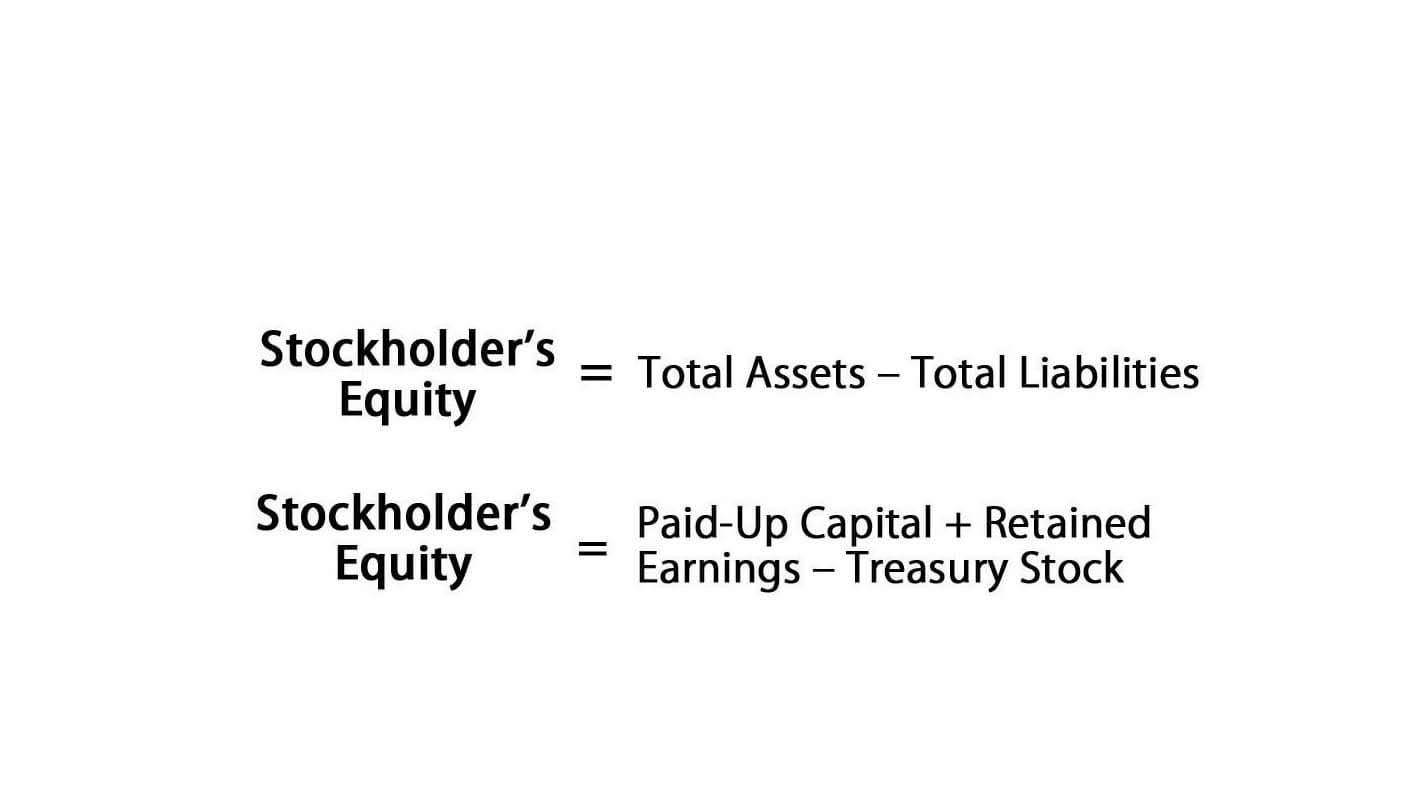
Like other financial statements, a retained earnings statement is structured as an equation. Retained earnings can typically be found on a company’s balance sheet in the shareholders’ equity section. Retained earnings are retained earnings calculated by taking the beginning-period retained earnings, adding the net income (or loss), and subtracting dividend payouts.
- The difference in retained earnings is $50,000, meaning the company’s retained earnings increased by $50,000 from the previous fiscal year.
- These examples can give you a better idea of what calculations really look like and how these figures are leveraged in the real world.
- To determine this number, we look at all revenues and subtract related expenses, including cost of goods sold (COGS) and operating costs like salaries and utilities.
- This separate statement is also called a statement of owner’s equity and is essential in determining the amount of earnings that can be distributed to shareholders as dividends.
- The balance in the corporation’s Retained Earnings account is the corporation’s net income, less net losses, from the date the corporation began to the present, less the sum of dividends paid during this period.
Statement of Retained Earnings Formula:
- This ending retained earnings balance can then be used for preparing the statement of shareholder’s equity and the balance sheet.
- Retained earnings are a vital measure of a company’s financial health and performance in accounting.
- Remember, dividends reflect your company’s earnings distribution policy and significantly affect the financial statement scenario.
- The purpose of this statement is to provide information about a company’s retained earnings and how these earnings have changed over a specific period.
- Begin the statement by stating the opening balance and retained earnings amount carried over from the previous fiscal year’s end.
It’s also sometimes called the statement of shareholders’ equity or the statement of owner’s equity, depending on the business structure. Retained earnings offer valuable insights into a company’s profitability, growth potential, and financial decision-making. By examining retained earnings over time, investors and management can better understand how effectively a company reinvests profits for growth or rewards shareholders through dividends. For growing companies, a rising retained earnings balance often signals healthy reinvestment in the business. For established companies, a balanced approach between retained earnings and dividends can indicate a well-managed strategy to keep investors happy while fueling growth. A statement of retained earnings is a financial snapshot that tracks how your company’s retained earnings—those reinvested profits—change over a specific period, like a quarter or fiscal year.
An Example on How to Prepare a Statement of Retained Earnings for Financial Reporting Success
According to FASB Statement No. 16, prior period adjustments consist almost entirely of corrections of errors in previously published financial statements. Corrections of abnormal, nonrecurring errors that may have been caused by the improper use of an accounting principle or by mathematical mistakes are prior period adjustments. Normal, recurring corrections and adjustments, which follow inevitably from the use of estimates in accounting practice, are not treated as prior period adjustments. Also, mistakes corrected in the same year they occur are not prior period adjustments. A company indicates Budgeting for Nonprofits a deficit by listing retained earnings with a negative amount in the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet. The firm need not change the title of the general ledger account even though it contains a debit balance.
